At the moment, leaves are the bane of my life.
They drift down in their tens through the day. The lawns, porch and verandahs are no sooner swept that they come drifting down to make a mess, yet again.
And Saturday, when Bangalore was hit with unexpected torrential rains, our house almost flooded because fallen leaves had covered the water outlets on our terrace and there was a good six inches accumulated before we realized it and cleared the outlets. A few more minutes and the water would have entered the house.
But in general of course, who doesn’t love leaves: the variety of the shades of green, their shapes and sizes, the shadows they cast, the way they rustle in the breeze or when birds and squirrels play among them.
There are some people who take this love and appreciation to aesthetic heights. They are the leaf-artists.
Some people of course consider the leaf itself as art.’ There is artistry to a leaf that I find hard to put into words. In looking at leaves, the colours and veining, the patterns and textures, I get a good feeling. Leaves are nature’s artistry on display’, says Hank Erdmann, a leaf-photographer.
Others use the leaf as the medium. These leaf-artists express themselves through various creative expressions using leaves. This spans leaf printing, leaf carving, leaf painting and leaf collage. All of these are based on highlighting the leaf’s natural colours, shapes and textures.
It is likely that leaf-art is as old as our cave-dwelling ancestors. One can easily imagine our grandnmother picking up a leaf and carving a design on it with a sharp stone. And from these projects must have emerged the use of leaves as a medium for writing on—palm leaves were used for writing since the 5th century BCE in India. The ephemeral nature of the medium however has not left much proof of art on leaves.
But two contemporary artists have taken leaf-art to a new level.
The first is the Colombo Ecuadorian photographer, Yinna Higuera. Her recent collection ‘Traces’ is a series of portraits of rural Ecuadorian women, made on banana, cocao, coffee and other leaves. The collectoin documents the lives of these women, and portrays their link with nature and its cycles. The exhibition has been shortlisted for a Sony World Photography award, 2025. This is based on the technique of ‘chlorophyll printing’. The images are printed leveraging the leaf’s photosensitivity, merging photography with nature. This is an alternative photographic process where photographic images are developed on natural leaves through the action of photosynthesis, and goes back to the 19th century.
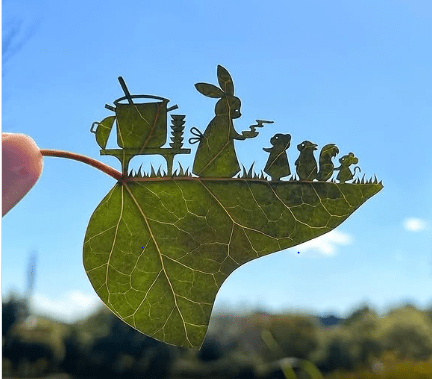
Another artist making waves (or gentle breezes) with his leaf art is Lito, a Japanese artist. He uses a completely different technique. He carefully selects a leaf, makes an intricate drawing on it, and painstaking carves it. The scenes often depict animals, birds and landscapes. Lito makes one leaf-carving every day! For him, this is not just a means of artistic expression, but also a way of managing his ADHD. It helps him focus, be calm–he sees it as a form of meditation. And importantly for him, leaf-carving is a means of earning a livelihood.
So I am going to re-calibrate. And appreciate each leaf as it drifts down to land on my verandah. Before muttering irritably at it!
And to end, here is a poem on leaves by Sarojini Naidu, whom Mamata wrote about a few weeks ago:
Like a joy on the heart of a sorrow,
The sunset hangs on a cloud;
A golden storm of glittering sheaves,
Of fair and frail and fluttering leaves,
The wild wind blows in a cloud.
Hark to a voice that is calling
To my heart in the voice of the wind:
My heart is weary and sad and alone,
For its dreams like the fluttering leaves have gone,
And why should I stay behind?
–Meena
PS: Today there are even Leaf Engraving Machines, ‘specialized for intricate leaf designs, perfect for crafting unique art pieces!’
The picture is from Lito’s Instagram page, art_dailydose


