This year is supposed to mark 90 years of one of the world’s most popular board games—Monopoly. It is estimated that the game, translated into 47 languages, has been played by one billion people worldwide. Hasbro, the company that produces the game is marking the milestone with events and publicity that retells the story of the invention of the game, and its subsequent success that made history.
According to this version, the game was originally created in 1935 by Parker Brothers. As the story goes, in 1932, a Philadelphia businessman named Charles Todd and his wife, Olive, introduced their friends Charles and Esther Darrow to a real-estate board game they had recently learned. The board game involved rolling dice to move tokens across the board while buying up properties listed on the board. The game did not have a name, and was not marketed but passed from friend to friend who all enjoyed playing it. Charles Darrow, who was at the time unemployed and in need of money, saw a potential opportunity, and asked his friend Todd for the written rules. There were none, friends made up rules as they played. It was informally known as the ‘monopoly game’.
Darrow however put together these ‘rules’ and hired an artist to design a board, and tokens and began to hand produce sets which he sold to a local department store with the name Monopoly. The game was a hit. Darrow sold this version to the toy manufacturer Parker Brothers in 1935, claiming that it was entirely his invention. He was granted a patent for this in 1935. And thus the official time line for the origin of game was pegged by Parker Brothers at 1935, and Monopoly was marketed with the story of how a struggling salesman created the game in his basement to support his family during the Great Depression.
However, the real origin of the game goes back much further, to the beginning of the century, and its creator was a woman who was a pioneer in more fields than one. Born in Illinois in1866 to Scottish immigrant parents Elizabeth Magie moved to Washington DC in her early 20s. Lizzie, as she was known to her friends, lived as a single woman supporting herself, working as a stenographer and typist, both unusual for a woman in those times. Not only did she live on her own, she saved up and bought her own home, and went on purchase some acres of property. She also wrote poetry and short stories, and did comedic routines onstage. Lizzie had strong and radical political views. This was a time of mighty monopolies which led to huge income disparities. Lizzie became interested in the anti-monopolist policies of Henry George a politician and economist who propagated the concept of a single “land value tax”. The general idea that instead of taxing income or other sources, the government should only tax land, based on the usefulness, size, and location of the land, thus shifting the tax burden to wealthy landlords. The government should use the money from the collected taxes for its essential functions and distribute the rest to people in the lower socio-economic segment. His message resonated with many Americans in the late 1800s, when poverty and squalor were widespread in the cities.
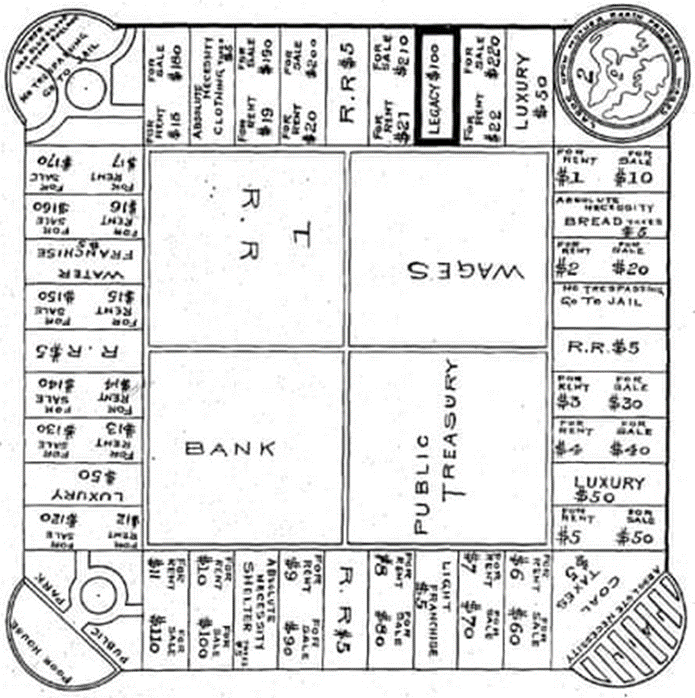
Lizzie was looking for an interactive and creative way to teach Henry George’s economic theories to friends and colleagues. The twentieth century had just dawned, and board games were becoming popular in middle-class homes. Many inventors realized their potential not just as a form of recreation, but as a means of communication. Elizabeth Magie felt that a board game could do what she visualized. After her office hours, Lizzie sat at home night after night thinking and drawing, rethinking and redrawing the grid and messages that would communicate these radical concepts.
Most of the board games at that time had a linear path design. Lizzie’s game had a grid that went round the board. The game featured play money and deeds and properties that could be bought and sold. Players borrowed money, either from the bank or from each other, and they had to pay taxes. In one corner were the Poor House and the Public Park, and across the board was the Jail. Also included on the board were three words scrawled across: GO TO JAIL.
Lizzie Magie created two sets of rules for her game: an anti-monopolist set in which all were rewarded when wealth was created, and a monopolist set in which the goal was to create monopolies and crush opponents. Her dualistic approach was a teaching tool meant to demonstrate that the first set of rules was morally superior. Ironically it was the monopolistic version of the game that caught on.
Lizzie called this game the Landlord’s Game. She described the new concept thus: “It is a practical demonstration of the present system of land-grabbing with all its usual outcomes and consequences,” she wrote in a political magazine.
She was in her thirties when she applied for a patent for her game in 1903. At that time she represented the less than 1 percent of all patent applicants who were women. And this was three decades before Parker Brothers started manufacturing Monopoly for which Darrow claimed credit as inventor, and Darrow’s story of a fluke invention by an unemployed man grew into the legend of Monopoly (and earned him millions).
While some people noted the similarity between Monopoly and the Elizabeth Magie’s Landlord’s Game, the Darrow legend continued. A newspaper story in 1936 aroused interest when it reported on the similarity, and also that in 1935 (when Monopoly got its patent) Lizzie had sold her board game patent rights to Parker Brothers for only $500 and no royalties. Elizabeth Magie never got due credit for her invention, and she died in relative obscurity in 1948.
With its iconic design elements, the paper money, the property names, the tokens and the rush of ‘buying and selling’, ‘making deals’ and ‘undisguised competition’ Monopoly’s popularity continues even a century later. Its origins which were based in the critique of landlords have been obscured as the game has come to represent the blatant pursuit and accumulation of wealth. The words of the mother of its invention Elizabeth Magie still resonate: “It might well have been called the ‘Game of Life’, as it contains all the elements of success and failure in the real world, and the object is the same as the human race in general seem[s] to have, i.e., the accumulation of wealth.”
–Mamata
