When we think of great explorers, we picture men in naval uniforms, compasses in hand, charting “new worlds.” But tucked away in the annals of Australia’s history is a story that breaks that mould. It’s the story of Bungaree—the first Aboriginal man, and indeed the first Australian, to sail right around a continent.
His name is little known today, but his contribution to one of history’s most extraordinary voyages, in an exploration led by Captain Matthew Flinders, an English navigator was extraordinary.
From Broken Bay to the World
Bungaree was a man of the sea. Born around 1775 among the Kuringgai people near Broken Bay, north of Sydney, he grew up at a time when everything around him was changing. European ships had begun to appear on the horizon; new settlements were springing up on ancient lands. While many Aboriginal communities resisted the newcomers, Bungaree was curious. Quick-witted and charismatic, he learned to move between two worlds—his own and that of the British colonists.
By the time Flinders was preparing to embark on his grand voyage of exploration, Bungaree had already earned a reputation as a skilled sailor and interpreter. Flinders, who understood the need for a knowledgeable local person on his mission, invited Bungaree to join the expedition aboard HMS Investigator in 1801.
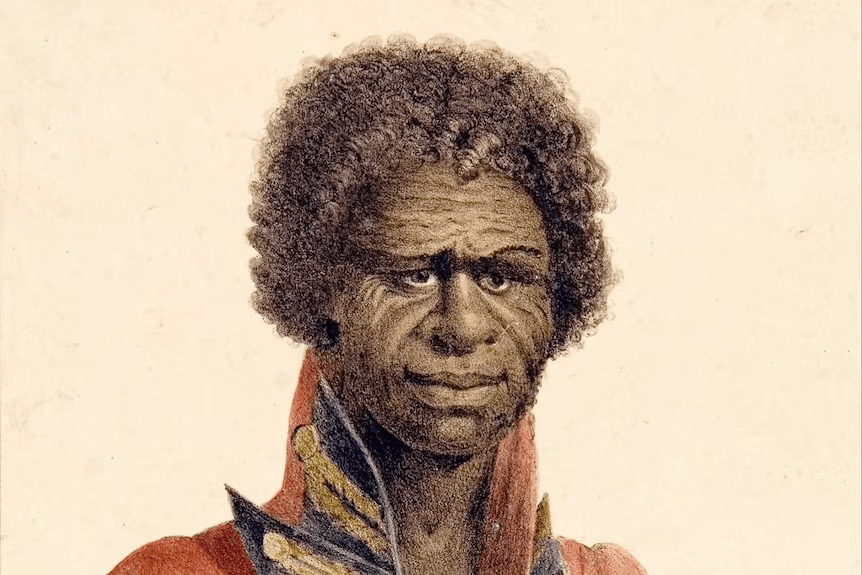

The Journey Around a Continent
The Investigator’s mission was to chart the entire coastline of the vast southern landmass known then as New Holland. Flinders hoped to prove it was a single continent—what we now call Australia. For this, he needed not just navigational skill, but also understanding—someone who could help bridge worlds. Bungaree became that person.
Throughout the voyage –from December 1801 to June 1803–Bungaree played a vital role as peacemaker and emissary. When the Investigator anchored near Indigenous communities, it was often Bungaree who stepped ashore first—speaking to local groups in shared gestures, explaining the strangers’ peaceful intent, and easing tensions that could have turned deadly. His presence gave the expedition a human connection that maps and compasses could not.
Flinders, for his part, admired Bungaree’s warmth and humour. In his journals, he wrote that Bungaree “was always of service wherever we went,” and that his “good disposition and open, manly conduct” won respect from both shipmates and the people they met. It was a rare acknowledgment of partnership in an age otherwise defined by hierarchy and conquest.
The Man Beyond the Maps
The voyage was gruelling. The Investigator battled storms, leaks, and disease. Food was scarce; scurvy stalked the crew. Yet through months at sea and thousands of kilometres of unknown coast, Bungaree remained cheerful and steadfast—a figure of resilience and adaptability. When they finally completed the first circumnavigation of the continent in 1803, Bungaree had travelled more of Australia’s coastline than any person before him.
And yet, history gave him only a passing mention. While Flinders returned to England (and was later imprisoned by the French), Bungaree returned to Sydney. There he became something of a local character—always dignified, dressed in military uniforms, wearing his medals proudly. He was lovingly referred to as “King Bungaree,”.
An Amazing Feat
So this was the veryfirst successful circumnavigation of an entire continent in recorded history–the first time anyone had completely circumnavigated a single, continuous continental landmass on Earth.
Other earlier famous circumnavigations (like Magellan’s) went around the globe or around islands (for example, Tasmania, which Flinders himself had circumnavigated earlier with George Bass in 1798). But going around a continent — that is, a vast mainland connected by continuous coastline — was unique. (Incidentally, while one can circumnavigate Africa, the Americas through the Panama Canal, and Antarctica when the ice permits, it is not possible to circle Asia and Europe).
Remembering Bungaree
Bungaree died in 1830 and was buried at Rose Bay. His resting place, like so much of his story, is unmarked. But in recent years, there has been a growing recognition of his contribution—not just as a companion to Flinders, but as a symbol of the spirit of adventure, resilience, and bringing two worlds together.
–Meena
PIC from ABC News